Which is the difference between a solid propellant engine and a liquid propellant engine? Let’s see which are the pros and the cons of these two rocket engines!
Solid Propellant Rocket
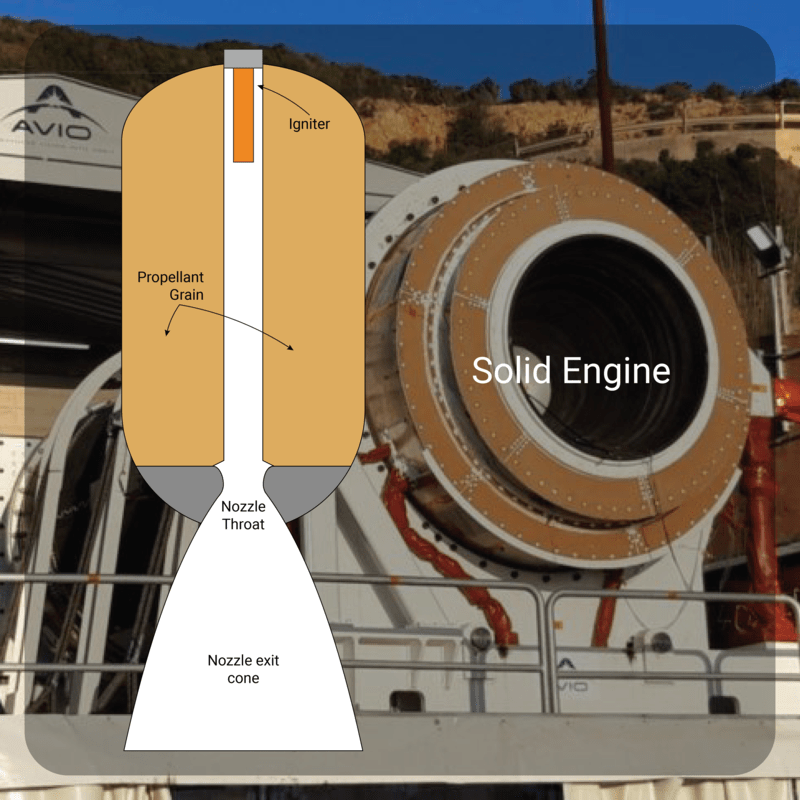
The solid propellant rocket engine is a simple engine because it has no feed systems or valves. This is due to the fact that the grain (the solid propellant) to be burn is stored in the combustion chamber. Once ignited, it is designed to burn smoothly at a predetermined rate on the exposed internal grain surfaces. The hot gasses, resulting from the ignition, pass throughout the nozzle creating thrust. The combustion proceeds until all the propellant has been consumed.
Solid rockets provide a huge amount of thrust and thus they are usually used as boosters.
Pros: Simple, high thrust, low specific impulse, good storability.
Cons: No shutdown, no thrust regulation, high mass.
Vega is one of the launchers using solid rocket engines in its first three stages, called P80, Zefiro 23 and Zefiro 9, while the last one, AEVUM, is a liquid rocket engine.
Liquid Propellant Engine
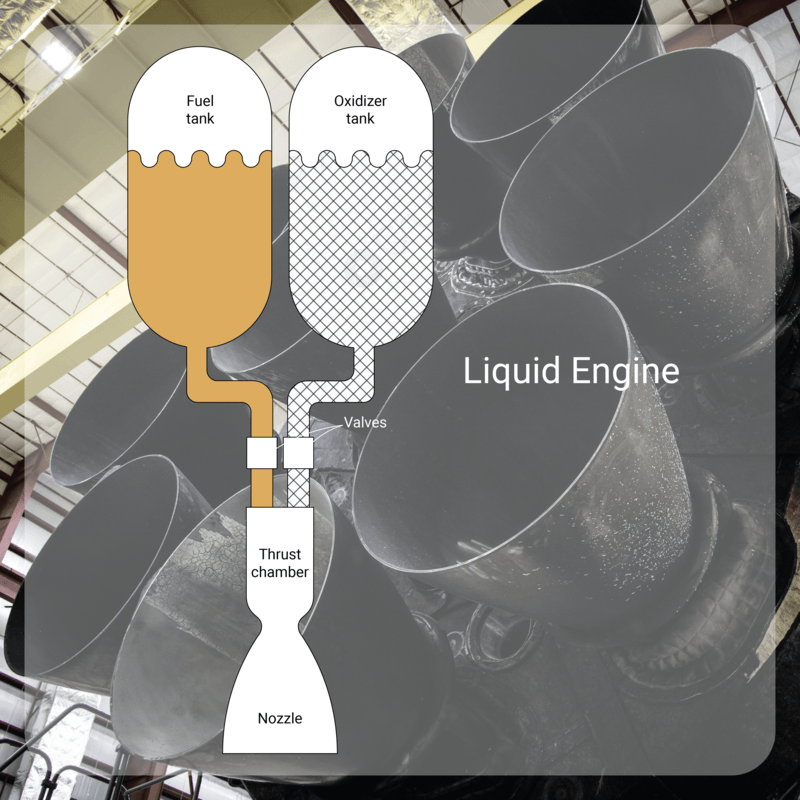
A liquid propellant rocket has both the fuel and the oxidizer in a liquid form in the tanks. Liquid rockets use propellants stored as liquids that are fed under pressure from tanks into a thrust chamber, where they react to form hot gases, and, finally, the gases are accelerated through a supersonic nozzle.
The engine needs to have several precision valves and complex feed mechanisms to garantee the proper functioning of all the components.
The liquid rocket engines permit repetitive operations, like restart and shut down.
Pros: Thrust can be controlled, re started and shut down
Cons: Complex (pumps and valves).
As said before, Vega uses a liquid propellant fourth stage. This is due to the fact that with a liquid engine, the stage can be started and shut off at will. Falcon 9, instead, is a fully liquid propellant rocket, with 9 Merlin 1D in the first stage and a single Merlin Vacuum in the second stage.
| Engine | P80 – Vega | Merlin 1D (x9 engines) – Falcon 9 |
| Type | Solid Propellant Engine | Liquid Propellant Engine |
| Propellant | HTPB | LOX/RP-1 |
| Specific Impulse | 280 s – in vacuum | 311 s – in vacuum |
| Thrust | 3.015 MN – in vacuum | 7.686 MN – at sea level |