On Sep 12th, the Capsule of New Shepard activated its escape system to flee the explosion of its booster; the escape system saved the payload. Why was it necessary?
But, first of all, what is New Shepard? What was it designed for? We will go through Blue Origin’s New Shepard and, then, we will delve into the causes of the explosion.
Blue Origin’s New Shepard
We have met Blue Origin in our last Technical Capsule, Vulcan Centaur and New Glenn, presenting its under development orbital rocket; today, instead, we will investigate its little brother New Shepard. Just as New Glenn, New Shepard is named after a pioneer astronaut: Alan Shepard, the first American to go to space.
New Shepard is a suborbital single-stage rocket designed to take passengers and research payload over the Kármán line: the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, the FAI, impose the Kármán line at an altitude of 100 kilometers. As stated before, Blue Origin designed New Shepard for space tourism, and, so, it designed a pressurized and comfortable Crew Capsule. This Capsule has six seats for the passengers. Everyone has its own large window to enjoy the 11-minutes flight.
Furthermore, New Shepard is at the forefront in ecology. Firstly, the rocket is the first and only fully reusable active rocket, with 99% of dry mass being reusable. Both the booster stage and the capsule are recovered from each launch; the boosters can fly more than 25 times. Secondly, the BE-3 engines, produced by Blue Origin, process clean LOX and LH2, which have only water vapor as a byproduct; therefore, the emissions are carbon-free.
New Shepard is a small rocket, only 18 meters, like Rocket Lab’s Electron. But its height is irrelevant, as it should not take heavy payloads at high altitude, but passengers and research payload in suborbital flight. The suborbital crew flights began on Jul 20th, 2021 with four passengers, among whom were Jeff Bezos, the founder of Blue Origin (and Amazon as well). Since then, other five crewed missions had success out of 23 missions. And speaking of the 23rd mission, that is the main topic of this post!
NS-23: The first failure of New Shepard
On Sep 12th, 2022, Blue Origin scheduled the NS-23 mission with 36 payloads on board from academia, research institutions, and students across the globe. There was no crew on board. New Shepard lifted off from Launch Site One in West Texas at 15:40 UTC; about one minute after liftoff, the booster failed and the capsule escape system was automatically activated, causing the capsule to get ejected far from the booster. The explosion happened at an altitude of 8.7 km and a speed of 1100 km/h, immediately after the Max Q, the maximum dynamic pressure (read Which are the main stages in a rocket launch? to have more information on Max Q); the booster hit the ground within the designed hazard area, with no injuries reported. For the full launch video, click here.
However the important fact is: what happened to the capsule? As said before, the capsule was ejected 2 km upwards. After reaching 11 km of altitude, the capsule fell in a free-fall for more than 3 km. After that the parachutes opened. The first parachutes are small and designed to counteract gravitational pull. In the last few meters before landing, the main parachutes were opened. Their goal is to decrease the speed of the capsule and guarantee a smooth landing.
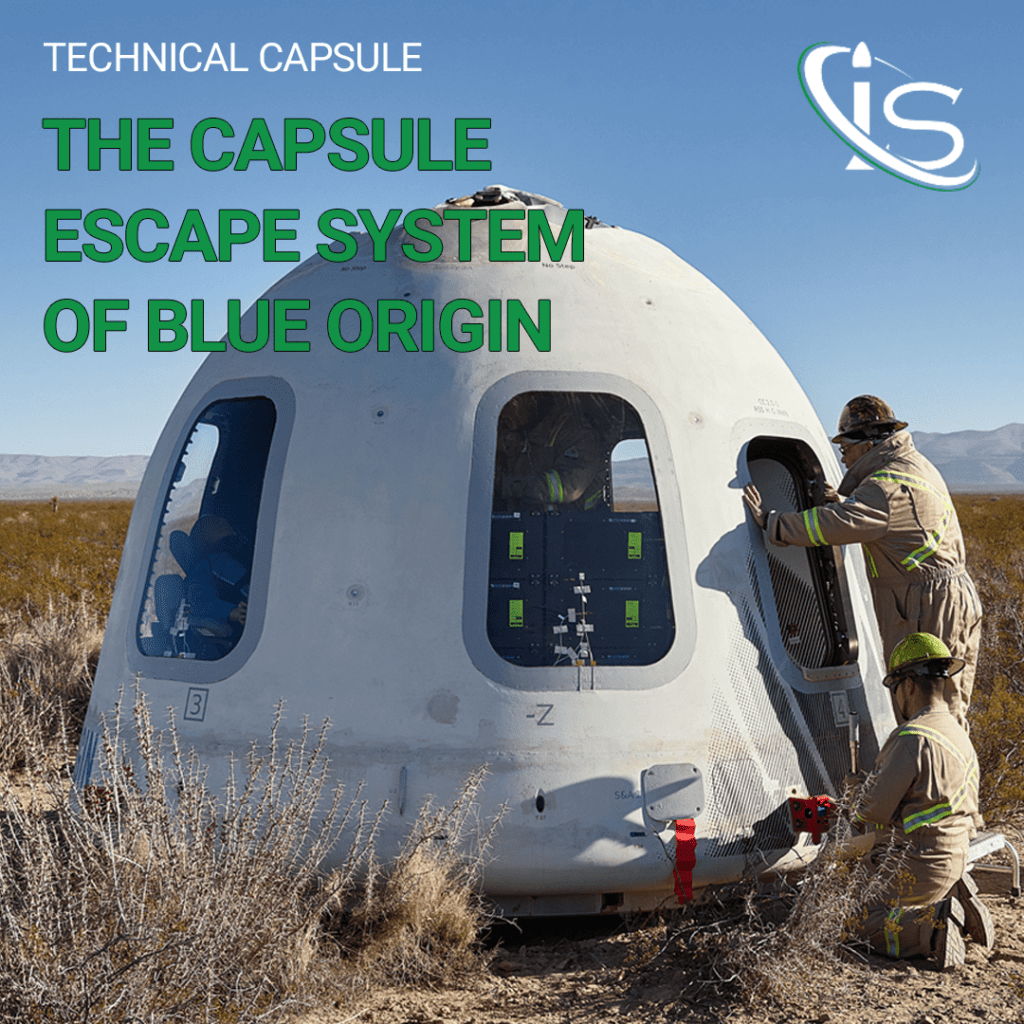
Capsule Escape System
This was the first time that the Capsule Escape System was necessary; but Blue Origin had successfully tested its functionality in three preceding tests:
- On Oct 19th, 2012, the Escape System was activated on the pad;
- In mission NS-6, on Oct 5th, 2016, the Escape System ejected the Capsule at Max Q;
- In mission NS-9, on Jul 18th, 2018, the Escape System was activated in space.
The failure of the booster has been the first major failure for Blue Origin, but the activation of the Capsule Escape System has revealed the reliable safety of the space travel with New Shepard. In mission NS-23, there were no passengers; but, if there had been, they would have been rescued.
The safety of New Shepard lays not only in the Escape System, but even the landing system; in fact, its design with multiple redundancies makes it more reliable. The capsule can land with just two among the three parachutes at its disposal. Moreover, the capsule has a retro-thrust system, which lands the capsule at just 1.6 km/h expelling a pillow of air. Even the seat of the passengers have been designed to flex and absorb g-forces.





